Remember this?
Problem statment for starters :
Consider this scenario. Any enterprise
application these days comprises of one to few moving components.
Moving components as in, components that are hosted on separate servers. A simple J2EE application which does basic CRUD
operation via an User Interface has 2 components.
- Server 1 - To hold the business logic and UI
- Server 2 - Database server.
Now, ideally, as a developer I would be
interested if there is a problem with either one of the components. I
would like to be notified if there is a problem. This problem has two parts to it.
1. To parse the Log messages.
2. Notify concerned parties.
1. To parse the Log messages.
About Logstash from the description (in their own
words)
Logstash is a tool for managing events
and logs. You can use it to collect logs, parse them, and store them
for later use(like searching)
It is fully and freely open source.
Comes with Apache 2.0 license.
Logstash's configuration consists of
three parts
Inputs – Where to look for logs? Log
source.
Filters – What are we looking for in
the given logs? Say, a particular exception or a message
Outputs – What to do once I find the
exception/message? Should I index it, should I do something else?
Then go ahead and configure it up front.
Logstash requires these things to be
configured in a *.conf file. And this file needs to be passed during
start up.
Sample test.conf file
input
{
file {
# Answers the question - Where? Logstash will look for files with the pattern catalina.*.log
# sincedb is a file which logstash uses to keep track of the log lines that has been
# processed so far.
type => "loglevel"
path => "D:/Karthick/Softwares/Tomcat/tomcat-7_2_3030/logs/catalina.*.log"
sincedb_path => "D:/logstash/sincedb"
}
}
filter {
grep {
# Answers the question - what are you looking for?
# In this example, I am interested in server start up.
# @message - maps to one log statement/event and I have defined a grep to match the word
# 'Server startup' in the message.
match => ["@message","Server startup"]
type => "loglevel"
}
}
output
{
stdout
{
# Answers the question - what to do if there is match?
# For now, we'll just output it to the console.
message=>"Grep'd message - %{@message}"
}
}
Steps:
- Download logstash jar from this location
.
- Place the jar inside a working directory (D:/logstash in my case) and
extract it.
- Copy the test.conf inside working
directory (D:/logstash)
- Open command prompt and navigate to the
working directory and run this command.
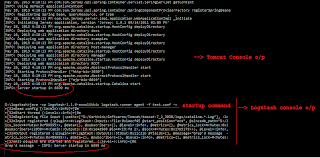
java -cp logstash-1.1.9-monolithic logstash.runner agent -f test.conf -v
Start local tomcat (since I've used
Tomcat logs as my source)
Next post : Monitor exceptions using logstash
Happy Coding :)
~ cheers.!
Happy Coding :)
~ cheers.!
No comments:
Post a Comment